do you want to install the electrical installation of your van and not get scorched in the attempt? Before getting down to work, you will have to familiarize yourself with a lot of terms, words and formulas that you will find everywhere: manuals, tutorials, youtube videos… Don’t worry, we have written this camper electricity dictionary to help you!
We have created it in the most simple and enjoyable way, with the terms that we have learned throughout our installation process and that we know will be useful to you too. Don’t wait any longer and recharge your batteries, energy self-sufficiency is waiting for you!
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
O
P
R
S
T
V
Absorption
This is the second charging phase of a battery. It begins when the absorption voltage is reached. In it the current slowly decreases until the battery reaches 100% of its capacity and its purpose is the recovery of the electrolyte that may have been disturbed if the battery has suffered deep discharges. Depending on the state of the battery, this stage will be longer or shorter to ensure its complete recovery.
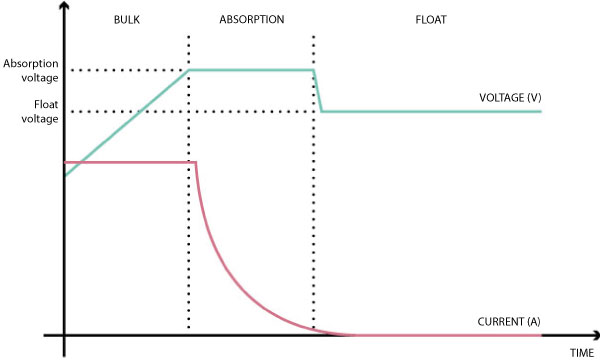
Read our article if you want to know which are the charging stages of a battery.
Absorption voltage
The absorption voltage is the voltage limit that a battery must reach during the charging process to pass from the initial state of charge or bulk to the absorption state.
Read our article if you want to know which are the charging stages of a battery.
AC motor
AC motors, as their name suggests, work with alternating current. Their operation is usually achieved by generating a rotating magnetic field, by means of a stator, which makes the motor rotate. The speed is usually controlled by varying the frequency of the applied current.
Accumulator
An accumulator is a device that is capable of storing energy, i.e. a battery.
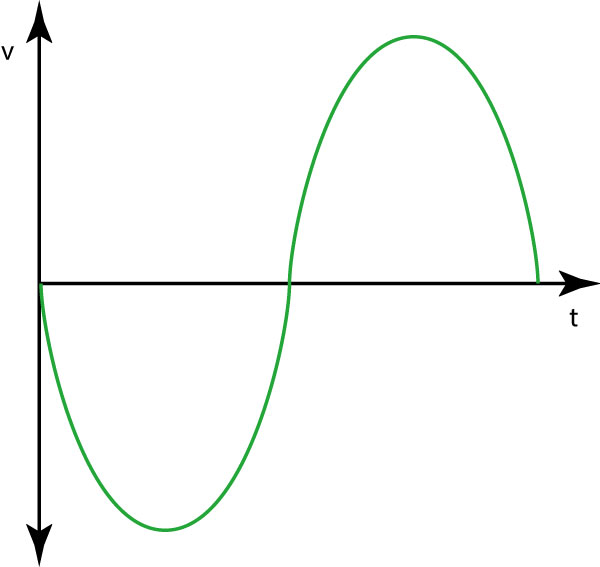
Alternating current
Alternating current is a type of electric current whose voltage varies at constant intervals in a cyclical manner, half the time it will be positive (the energy circulates in one direction) and the other half negative (it circulates in the opposite direction), normally forming a sine wave.
Booster
A booster is the way in which many people usually call a direct current converter. This device is used to transform a direct current, which has a voltage that is not stable, into another current, also direct, at a certain and stable voltage. It is often used to charge the auxiliary battery, in an optimal way, using the current generated by the alternator of the vehicle.
Read our article if you want to know more about relays, converters and boosters for campers.
Bulk
This is the first stage of battery charging. In it, energy is supplied to the battery at maximum intensity, so that its voltage increases rapidly until it reaches approximately 12.6V. From here it will charge more slowly until the first voltage limit (absorption voltage) is reached. At this point the battery will be between 80 and 90% charged.

Read our article if you want to know what are the charging stages of a battery.
Cable cross-section
The cross section of a cable is the area of a perpendicular section of the cable. Much attention must be paid to the correct sizing of cables, especially in direct current, to avoid overheating (due to the Joule effect) and voltage drops.
Read our article if you want to know how to size correctly the cables of your installation.
Capacity
The capacity of a battery is generally defined in the technical specifications by two pieces of information: its capacity (in Ah) and its discharge rate (in CXX). In order that it is understood better we are going to put the example:
- We have this Ultracell gel battery of 100Ah.
- In its data sheet it states the following:
- 100Ah C10.
- 115Ah C100h.
100Ah C10: This would mean that the battery is capable of delivering, during a continuous and stable discharge of 10 hours, a total of 100A. That is to say 10A during each hour, which would be equivalent to being able to power a device with a consumption of 120W for 10 hours.
115Ah C100Ah: In this case it would mean that the battery can give, during a continuous discharge of 100 hours, a total of 115Ah before being exhausted. Or what is the same, 1.15A during each hour. So a device consuming 13.8W for 100 hours could be used.
Charge/discharge cycle
A charge/discharge cycle is the process in which a battery charged to its maximum capacity goes to its maximum allowable discharge state. With each charge/discharge cycle a battery loses charge capacity, which causes its life span to decrease.
Read our article if you want to know how to recharge the auxiliary battery in a motorhome or camper.
Current
The intensity of electric current is the current flow or the amount of transmitic charge per unit time. Its magnitude, in the international system (SI), is the ampere (A), which is equivalent to one coulomb per second (C/s).
DC motor
DC or direct current motors, as the name suggests, operate with direct current by generating a magnetic field that causes a rotating motion. The speed of the motor can be controlled by changing the voltage applied to the motor winding
Differential switch
A residual current circuit breaker is an electromagnetic protection device used in alternating current installations to protect people against accidental electrical discharges, by direct or indirect contact.
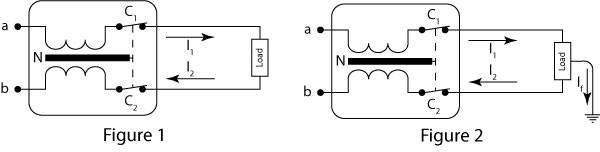
Figure 1 in the previous image shows a circuit with a residual current circuit breaker in a normal state. The current between point a and the load (I1) is equal to the current flowing from the load to point b (I2), therefore the magnetic fields created in the coils will be equal and opposite, canceling each other out.
On the other hand, in Figure 2, it can be seen that there is a leakage current (If), i.e. I1 will be greater than I2. Therefore, a non-zero magnetic field will be generated, which will attract and displace the core N, causing the contacts C1 and C2 to open, interrupting the current flow.
Read our step by step guide to make the 220V electrical installation in a camper van.
Direct current
Direct current is a type of electric current that is characterized by always maintaining the same polarity, that is, by always circulating in the same direction.
Discharge rate or discharge time
The discharge rate of a battery is the process of discharging its energy under certain conditions. For example, if you have a 100Ah C10 battery, it would mean that if you discharge the battery in a 10 hour discharge regime, it would be able to deliver a total of 100A.
Energy self-sufficiency
Energy self-sufficiency in a camper is the achievement of self-sufficiency in meeting your energy needs by adopting a strategy of reducing consumption and increasing the generation of clean energy, mainly by means of solar panels.
Read our article if you want to know how to be more energy self-sufficient with a proper solar installation.
Float
This is the last stage of battery charging. It is reached when the battery is already 100% charged and simply consists of providing the battery with only the current necessary to compensate for the loss due to self-discharge, so that its charge is maintained at 100%.

Read our article if you want to know which are the charging stages of a battery.
Frequency
The frequency of an alternating electric current expresses the number of wave cycles that are repeated during a given time. Its magnitude, in the international system (SI), is the hertz (Hz). One hertz represents the number of cycles repeated during one second. Most of the electrical energy generated in the world is at 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the country. There are also countries that have supplies at both frequencies.
Fuse
A fuse is a protective device consisting of a metal filament or foil with a low melting point. This device serves to protect points in an electrical installation as follows: If an increase in current intensity, above a certain value, were to occur, the filament or metal foil of the fuse would melt, due to the Joule effect, opening the circuit and stopping the passage of energy.
Hotspot
As the name suggests, a hotspot is an area, in this case referring to an area of a solar panel, where the temperature is higher than normal. This can lead to problems of varying severity:
- Decreased efficiency.
- Accelerated degradation of the plate materials.
- If we are talking about a flexible plate glued directly on a surface, it can cause damage to the material of this surface.
Read our article if you want to know the BEST way to install a flexible solar panel without risk of hot spots.
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s law was formulated by Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist and mathematician. It is a basic law that states the fundamental principles of electrical circuits. It states that the potential difference between two points of a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it and the resistance presented. It is given by the following formula:
V = I * R
Parallel connection
Two or more electrical elements are said to be connected in parallel if their input terminals are connected to each other and so are their output terminals. In the image a connection of three batteries in parallel is shown.
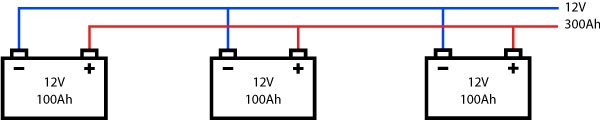
This is very useful when you want to maintain an independence in the power supply of each element and the same voltage at the input of each one.
Power
The electrical power is defined as the quantity of electrical energy that a certain element delivers or consumes during certain space of time, that is to say, the rate of energy transfer. Its magnitude, in the international system (SI), is the watt (W), which is equivalent to one joule per second (J/s).
Power consumption
Power consumption is the amount of energy used by one or more devices during a given period of time.
Use our consumption calculator to size your electrical installation correctly.
Power converter
It is an electrical device used to transform a direct current, which has a voltage that is not stable, into another current, also continuous, at a certain and stable voltage. It is usually used to charge the auxiliary battery, in an optimal way, using the current generated by the alternator of the vehicle.
Read our article if you want to know more about relays, converters and boosters for campers.
Power inverter
A power inverter is a device that transforms a direct current (DC) at a given voltage, which can be 12, 24, etc., into an alternating current (AC), in our case, at 220V, suitable for the use of conventional electrical and electronic devices.
Read our article if you want to know more about the best inverters for your van camper.
Reconditioning or Equalization
It is a stage of charge of a battery that consists of making a controlled overcharge of tension of the battery to obtain that the dissolution of the electrolyte is homogeneous and that all the cells have the same voltage.
Read our article if you want to know what are the stages of battery charging.
Relay
A relay is an electrical device that functions, very simply, as a switch that is electronically controlled. In the camper world, battery separator relays and power relays are widely used.
Read our article if you want to know more about battery separator relays.
Schuko
It is said plug, or socket, of type Schuko in a colloquial way to the system of socket defined as type F in the standard CEE 7. The system corresponds to the European standard with grounding and is formed by two cylindrical plugs (for the phase and the neutral) of 19mm long and 4,8mm of diameter, with a separation of 19mm between them. In addition, it has two contacts on two of the sides to connect the ground.
Series connection
Two or more electrical elements are said to be connected in series if they are connected one after the other. The image shows a connection of three batteries in series.
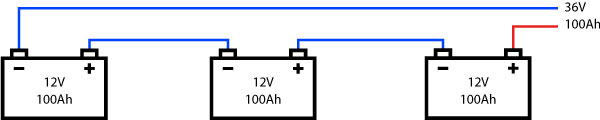
The circuits in series are very useful because they allow the sum of voltages, due to the fact that there is only one way for the current.
Shunt
A shunt is an electrical device that, in a camper, serves to extend the measurement limits of an ammeter. It is connected in series in the circuit to be measured and the ammeter in parallel to the shunt.
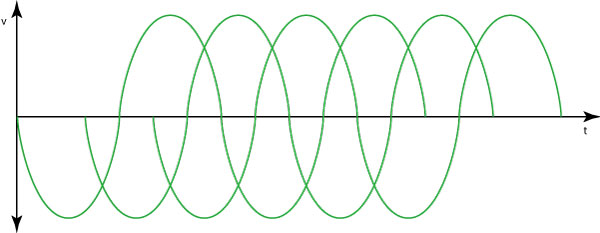
Single-phase current
Single-phase current is a type of alternating current that flows through a single conductor. The current of the conventional electrical system is a single-phase current. A single-phase system consists of three wires as follows, according to convention:
- Brown or black wire: Phase. The current flows through this wire.
- Blue wire: Neutral. It is the one in charge of closing the circuit and returning the current.
- Green and yellow wire: Grounding. It protects people from electrical risk if it is connected to ground.
Terminal block or terminal strip
A terminal block or strip is a type of electrical connector in which, using a screw, one or more wires are clamped against a metal part.
Thermal-magnetic circuit breaker
A thermal-magnetic circuit breaker is an electromagnetic protection device used in alternating current installations to protect the circuit from current surges, based, as its name suggests, on two effects of electricity: magnetic (Ampère’s law) and thermal (Joule effect). The switch consists of an electromagnet, which protects the circuit against short circuits, and a bimetallic sheet, which protects it against overloads, connected in series.
Read our step by step guide to make the 220V electrical installation in a camper van.
Three-phase current
Three-phase current is an alternating current electrical system consisting of three conductors through which current flows with an offset of 120°. An example of three-phase current is that originated in the alternators of cars. A three-phase system is made up of five wires as follows, according to convention:
- Black wire: Phase 1.
- Brown wire: Phase 2.
- Gray wire: Phase 3.
- Blue wire: Neutral. It is the one in charge of closing the circuit and returning the current.
- Green and yellow wire: Grounding. It protects people from electrical risk if it is connected to ground.
Voltage
Voltage is defined as the potential difference between two points. Its magnitude, in the international system (SI), is the volt (V).
